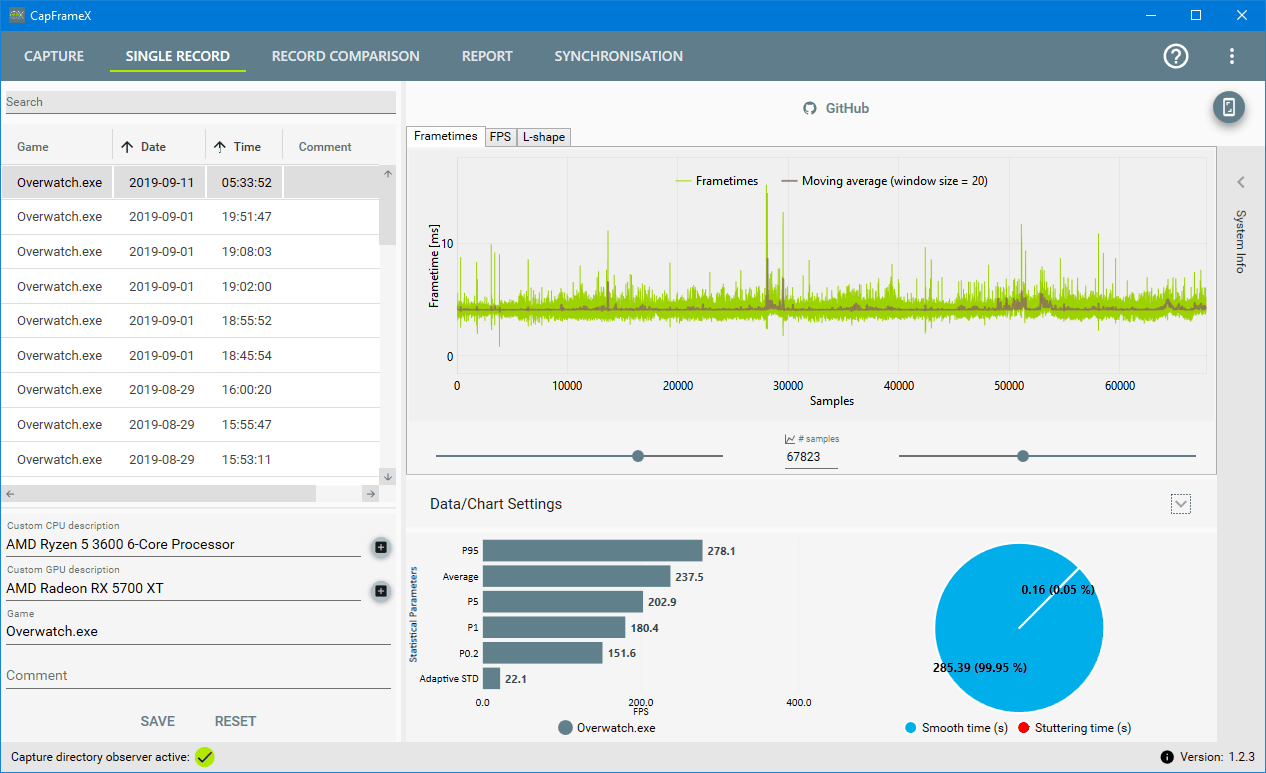
I don't think that's the case on the intel front. Look at this processor
Intel® Core™ i7-10510U Processor (8M Cache, up to 4.90 GHz) quick reference with specifications, features, and technologies.

ark.intel.com
The base clock is 1.8 GHz and the turbo is 4.9 GHz. Turbo is not a nice to have. This processor's clock speed more than doubles with turbo nad it is expected to play a big role on this processor.
Intel's doc's (below) clearly say if the load, temperature, and power consumption are ok that you will boost to turbo frequency.
'
Max Turbo Frequency
Max turbo frequency is the maximum single core frequency at which the processor is capable of operating using Intel® Turbo Boost Technology and, if present, Intel® Thermal Velocity Boost. Frequency is measured in gigahertz (GHz), or billion cycles per second.
'
Also 'Max Turbo Frequency refers to the maximum single-core processor frequency that can be achieved with Intel® Turbo Boost Technology. See
www.intel.com/technology/turboboost/ for more information. '
Maximum turbo frequency indicates the highest possible frequency achievable when conditions allow the processor to enter turbo mode. Intel® Turbo Boost Technology frequency varies depending on workload, hardware, software, and overall system configuration.
Due to varying power characteristics, some parts with Intel® Turbo Boost Technology 2.0 may not achieve maximum turbo frequencies when running heavy workloads and using multiple cores concurrently.
Availability and frequency upside of Intel® Turbo Boost Technology 2.0 state depends upon a number of factors including, but not limited to, the following:
- Type of workload
- Number of active cores
- Estimated current consumption
- Estimated power consumption
- Processor temperature
When the processor is operating below these limits and the user's workload demands additional performance, the processor frequency will dynamically increase until the upper limit of frequency is reached. Intel® Turbo Boost Technology 2.0 has multiple algorithms operating in parallel to manage current, power, and temperature to maximize frequency and energy efficiency. Note: Intel® Turbo Boost Technology 2.0 allows the processor to operate at a power level that is higher than its TDP configuration and data sheet specified power for short durations to maximize performance.
Find more information on Intel® products with Intel® Turbo Boost Technology ›
Processors with the same model number running under the same operating conditions may see some frequency or power variance. This is a natural characteristic of silicon driven by variances in voltages, power, and leakage during the production process. Contact your local Intel sales office or your distributor to obtain the latest specifications.