- Joined
- May 28, 2019
- Messages
- 10,231
- Reaction score
- 7,162
Image: NVIDIA
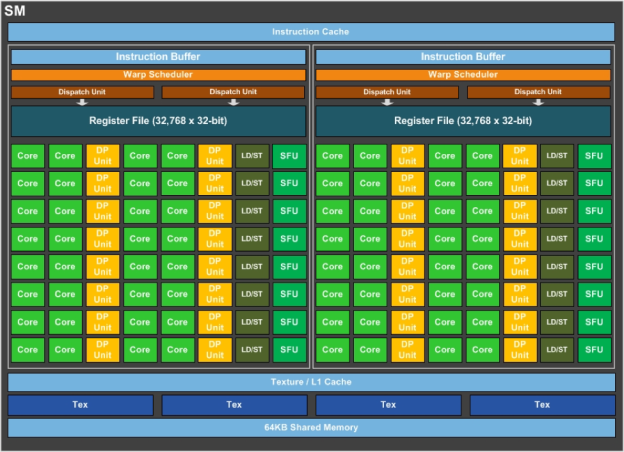
A research paper from NVIDIA illustrates how it could use new technology to improve ray tracing performance by up to 20% in future graphics cards. The authors begin by explaining that ray tracing “applications have naturally high thread divergence, low warp occupancy and are limited by memory latency,” and an “architectural enhancement called Subwarp Interleaving” could be one solution for performance gains.
Subwarp Interleaving allows for fine-grained interleaved execution of diverged paths within a warp with the goal of increasing hardware utilization and reducing warp latency. However, notwithstanding the promise shown by early microbenchmark studies and an average performance upside of 6.3% (up to 20%) on a simulator across a suite of raytracing application...
Continue reading...